
Per generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP), businesses amortize intangibles over time to help tie the cost of an asset to the revenues it generates in the same accounting period. For tax purposes, the cost basis of an intangible asset is amortized over a specific number of years, regardless of the actual useful life of the asset (as most intangibles don’t have a set useful life). The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) allows intangibles to be amortized over a 15-year period if it’s one of the ones included in Section 197.
Internal Revenue Code (IRC) and Patents
The overpayment by Microsoft is not necessarily a bad business decision, but rather the premium or value of those intangible assets that LinkedIn owned and Microsoft wanted. The $21 billion difference will be listed on Microsoft’s balance sheet as goodwill. The most common way to do so is by using the straight line method, which involves expensing the asset over a period of time. Amortization is calculated by taking the difference between the cost of the asset and its anticipated salvage or book value and dividing that figure by the total number of years that it will be used.
Amortization vs. Depreciation
Corporations amortize a patent utilizing its useful life, although a patent is legally valid for 17 years. The first method used to calculate the operation section is called the direct method, which is based on the transactional information that impacted cash during the period. To calculate the operation section using the direct method, take all cash collections from operating activities, and subtract all of the cash disbursements from the operating activities. A company should capitalize costs when a patent application has been submitted and such costs can be directly linked to a specifically identifiable patent that is likely to be granted. While copyrights have a finite life span of 70 years beyond the author’s death, they are amortized over their estimated useful life. The receipt of a cash dividend of $1,200 may be classified as either operating or investing cash inflow if financial statements are prepared in accordance with IFRSs.
Fundamentals of Intangible Assets
Take the case of a small tech company with a groundbreaking software algorithm; by patenting it, they can increase their valuation and attract venture capital. The initial cost of a patent also includes non-refundable purchase taxes and import duties, if applicable. These are considered part of the cost of preparing the asset for its intended use. Conversely, any trade discounts or rebates received are deducted from the gross cost to arrive at the net amount that is capitalized. In application, the prices of acquiring a patent could be so small that they don’t meet or exceed an organization’s capitalization restriction. In many bigger firms with larger capitalization limits, patents are hardly ever recorded as property except when they’ve been bought from different entities.
Determine How Long Patent Will Generate Revenue
The patent is being amortized over its economic useful life of 5 years using a straight-line method. On December 31, 2023, the company’s income statement showed a net income of $350,000. Over a period of time, the costs related to the assets are moved into an expense account as the useful life of the asset dwindles.
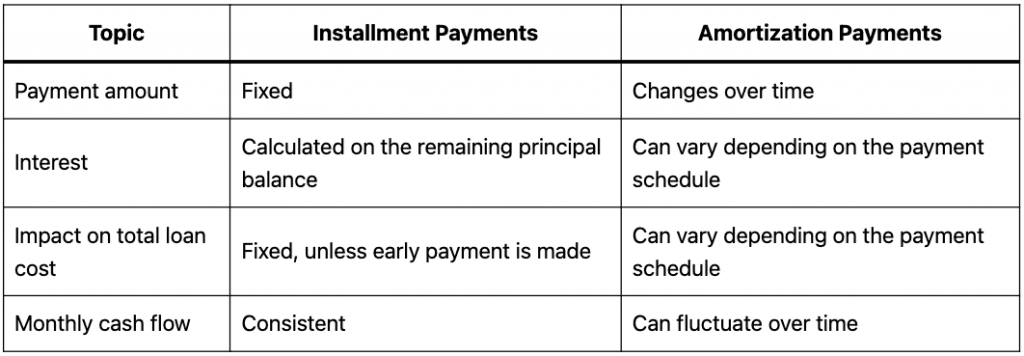
- In either case, the process of amortization allows the company to write off annually a part of the value of that intangible asset according to a defined schedule.
- The costs incurred to acquire or register a patent can be capitalized if they meet the criteria for asset recognition.
- Positive cash flow indicates that a company has more money flowing into the business than out of it over a specified period.
- Once capitalized, these expenditures become part of the patent’s carrying amount on the balance sheet.
If a patent does not supply worth, or supplies a decreased degree of worth, it is important to acknowledge the impairment and scale back or get rid of the carrying quantity of the asset. Updates to your application and enrollment status will be shown on your account page. We confirm enrollment eligibility within one week of your application for CORe and three weeks for CLIMB. HBS Online does not use race, gender, ethnicity, or any protected class as criteria for admissions for any HBS Online program.
Your organization must debit amortization expenses for $10,000 and credit score goodwill for $10,000 yearly for the next five years. Other intangible properties that have indefinite life spans are usually not amortized; however, they are evaluated for relevancy and risk. If these properties do not decrease in relevance or experience ruin of any kind, the indefinite life property will stay on your balance sheet indefinitely. An instance of an indefinite life, unamortized asset could be a digital music service. So long as the service is free from ruin and continues to be economically relevant, it stays on a balance sheet.
The amortization expense is then charged to the company’s income statement, decreasing the net income of the period. The accumulated amortization will also be presented in the balance sheet as a contra-asset forms and instructions account and will be reduced the carrying amount of patent. For tax reporting purposes in an asset sale/338(h)(10), most intangible assets are required to be amortized across a 15-year time horizon.
The valuation of a patent at the initial recognition stage also takes into account any government grants or subsidies received, which may reduce the overall cost attributed to the asset. It’s important to note that only the amounts that are directly attributable to the patent’s development and acquisition are capitalized. This means that general administrative expenses or overhead costs are typically not included in the patent’s initial measurement. Intangible properties are assets an organization owns that have worth but are not physical. Common intangible properties inside an organization include patents, logos, and franchise licenses. Amortization is the method of allotting the price of an intangible asset over its useful life.
This is an ideal situation to be in because having an excess of cash allows the company to reinvest in itself and its shareholders, settle debt payments, and find new ways to grow the business. To facilitate this understanding, here’s everything you need to know about how to read and understand a cash flow statement. This exclusive right enables the owner to manufacture, sell, lease, or otherwise benefit from an invention for a limited period. Explore Apple, Inc.’s U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission 10-K Filing for notes that discuss goodwill and whether Apple has had to adjust for the impairment of this asset in recent years. It is just an illustration, not a complete list of all cash inflows and outflows that may result from the investing activities of a company.
Revenue recognition for patent licensing must adhere to accounting standards such as ASC 606, which outlines a five-step model for recognizing revenue from contracts with customers. This ensures that revenue is recognized in a manner that reflects the transfer of control and the economic benefits derived from the patent. Companies must regularly assess whether the carrying amount of a patent exceeds its recoverable amount.
